Data collection is the bedrock of informed decision-making, letting organizations understand their impact, identify areas for improvement, and drive meaningful change. This is especially important in sectors like healthcare, education, and social development, where understanding complex realities is key to effective programs.
There are two main types of data collection methods – qualitative and quantitative:
Qualitative data dives deep into the “why” behind the numbers, capturing rich narratives, perspectives, and experiences through methods like interviews and focus groups.
Quantitative data provides the “what” – quantifiable measurements and statistics gathered through surveys, assessments, and other structured approaches.
Each method offers valuable insights, but combining both allows for a more holistic understanding.
Understanding Qualitative and Quantitative Data
Qualitative Data:
This type of data explores subjective experiences, opinions, and underlying reasons. It’s descriptive and often textual, gathered through methods like:
- In-depth interviews: One-on-one conversations to explore individual perspectives.
- Open-ended surveys: Surveys that allow respondents to provide detailed answers in their own words.
- Focus group discussions: Moderated group discussions to gather diverse viewpoints.
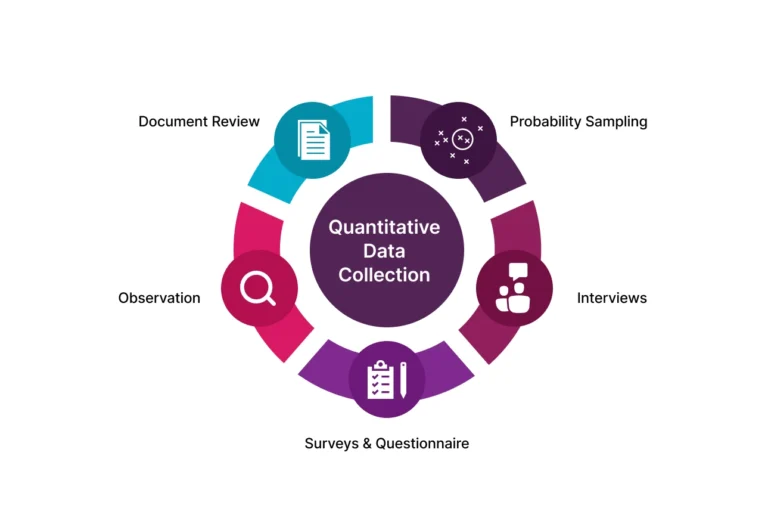
Quantitative Data:
This type of data deals with objective, measurable information. It’s collected through methods like:
- Surveys with scales: Surveys using scales (e.g., Likert scales) to quantify opinions and attitudes.
- Statistical data: Numerical data on program outcomes, demographics, or other measurable indicators.
- Numerical measurements: Physical measurements like height, weight, or test scores.
Why Combine Qualitative and Quantitative Data?
A mixed-methods approach, combining both qualitative and quantitative data, provides a more nuanced understanding of a situation. Here’s why:
- Richer insights: Qualitative data adds depth and context to quantitative results, explaining the “why” behind the numbers.
- Addressing limitations: Each method has limitations. Combining them helps overcome these weaknesses, creating a more robust and reliable dataset.
- Holistic understanding: Integrating both data types leads to a more complete picture of the issue being studied.
The Role of Digital Tools in Data Collection
Digital tools offer improved efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. Examples include:
- Survey platforms: Online tools like SurveyCTO and CommCare that facilitate the creation and distribution of surveys.
- Interview software: Platforms that allow for recording, transcribing, and analyzing interviews.
- Mobile data collection apps: Applications that enable data collection on mobile devices, even in remote settings.
Benefits of digital tools:
- Scalability: Easily collect data from large populations.
- Accuracy: Reduce errors associated with manual data entry.
- Ease of analysis: Digital tools often include features for data cleaning, analysis, and visualization.
Best Practices for Combining Data Collection Methods Using Digital Tools
Designing Your Study:
- Clear research questions: Define specific research questions that require both qualitative and quantitative data to answer.
- Integration plan: Determine how and where qualitative and quantitative data will be integrated.
Data Collection Tools:
- Qualitative tools: Utilize tools like transcription software, interview recording apps, and focus group platforms.
- Quantitative tools: Employ survey builders, analytics software, and data visualization tools.
- Integrated tools: Consider mobile data collection apps that can handle both qualitative and quantitative data, streamlining the process.
Ensuring Consistency and Compatibility:
- Harmonize data formats: Ensure data is collected and stored in compatible formats.
- Compatibility for analysis: Plan for how different data types will be analyzed together.
Integrating and Analyzing Combined Data
- Analysis methods: Explore various methods for analyzing mixed data, such as thematic analysis for qualitative data and statistical analysis for quantitative data.
- Digital tools for integration: Use integrated dashboards and advanced analytics tools to combine and visualize both data types.
- Drawing conclusions: Develop strategies to synthesize findings from both data types and draw meaningful conclusions.
Effectively combining qualitative and quantitative data requires careful planning, the right digital tools, and appropriate analysis methods. By embracing this holistic approach, you can unlock richer insights and drive more impactful action.